Camera Trapping in the Indian Forests: An Innovative Tool for Wildlife Conservation and Safari Adventures
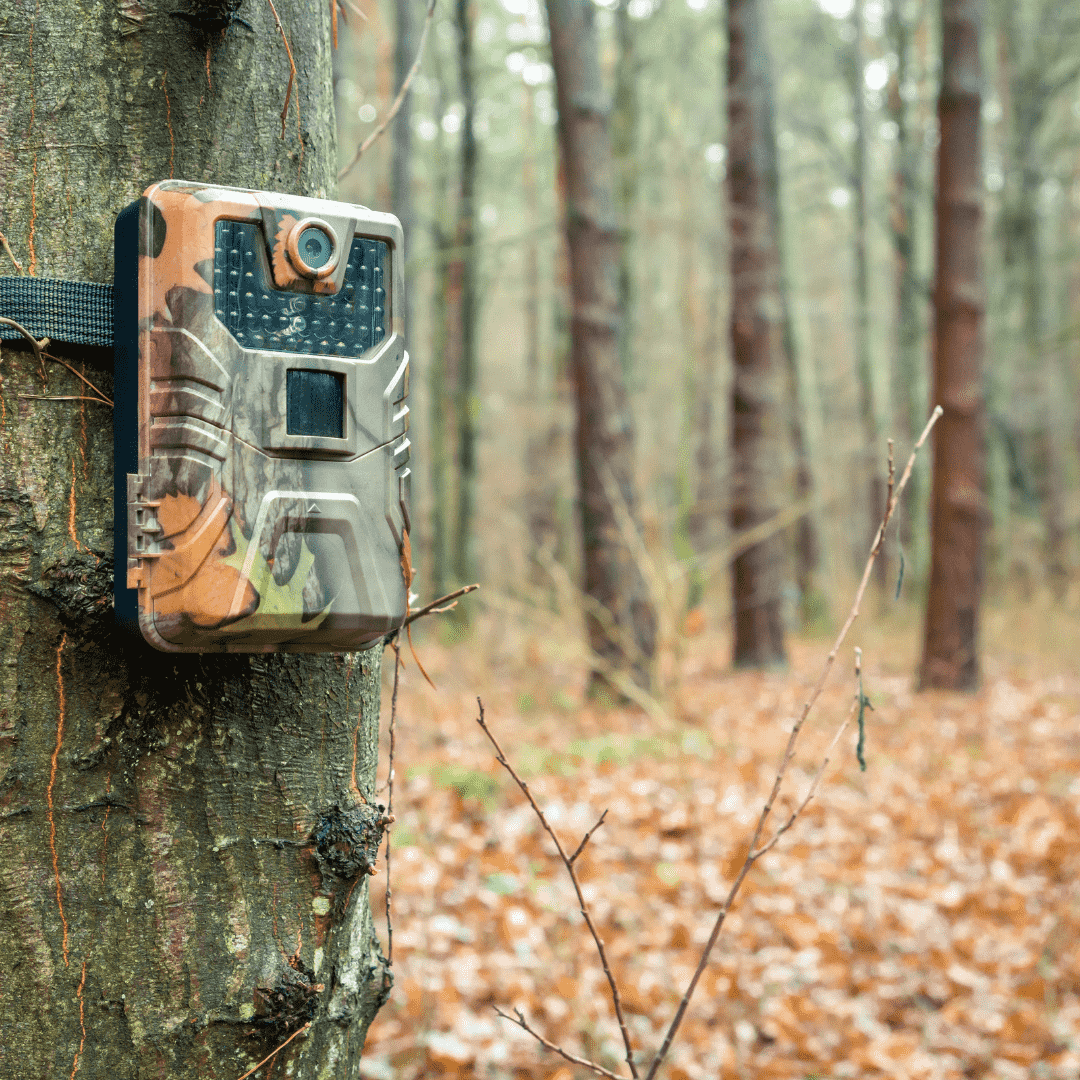
Camera trapping is a cutting-edge wildlife monitoring technique that has revolutionized the way wildlife researchers and conservationists study and protect animals in their natural habitats. This innovative method involves strategically placing motion-activated cameras throughout the wilderness, capturing candid and unobtrusive images of wildlife as they go about their daily lives. In India, camera trapping has emerged as a critical tool for the Forest Department across National Parks, aiding in wildlife conservation efforts and even assisting in the fight against poaching. Moreover, it has also become a fascinating activity for tourists during their safaris, offering them a chance to immerse themselves in the wonders of the wild and contribute to the protection of India's diverse and precious fauna.
I. Camera Trapping: A Technological Marvel
Camera trapping relies on sophisticated technology to monitor wildlife. The cameras are usually equipped with infrared sensors or heat/motion detection, ensuring that they are triggered when an animal passes nearby. As a result, they capture high-quality images and videos without human interference, allowing researchers to observe natural behaviors and gather valuable data without causing any disturbance to the animals.
II. Contributions to the Forest Department
The Forest Department across Indian National Parks has adopted camera trapping as an invaluable tool for several reasons:
Biodiversity Assessment: Camera trapping aids in conducting comprehensive biodiversity assessments, helping identify the presence and distribution of various animal species within a particular region. This information is crucial for understanding the overall health of the ecosystem and developing targeted conservation strategies.
Population Monitoring: By analyzing the images and videos captured, researchers can estimate population sizes and track population trends of different species over time. This data is essential for making informed decisions about conservation priorities and management practices.
Behavioral Studies: The non-intrusive nature of camera trapping allows researchers to observe animal behaviors in their natural habitat without causing stress to the animals. This insight into the daily lives of wildlife aids in understanding their ecological roles and assists in crafting better conservation measures.
Identification of Threats: Camera traps can reveal various threats to wildlife, including habitat destruction, illegal hunting, and poaching. This information allows the Forest Department to focus its efforts on addressing these issues effectively.
Monitoring Rare and Elusive Species: Camera trapping has proven particularly useful in detecting and monitoring elusive and rare species that are challenging to observe directly. This includes big cats like tigers and leopards, which are vital indicators of a healthy ecosystem.
III. Assisting in Combating Poaching
Camera trapping has become a valuable ally in the fight against poaching in Indian forests. Poaching poses a significant threat to endangered species, such as tigers, rhinoceroses, and elephants. By strategically placing camera traps in areas with a history of poaching or in locations where vulnerable species frequent, the Forest Department can collect evidence of illegal activities and track down poachers more effectively.
The images and videos captured by camera traps can serve as crucial evidence in court, aiding in the prosecution of poachers and strengthening legal cases. Moreover, the mere presence of camera traps acts as a deterrent, warning potential poachers that they are being monitored and increasing the risks associated with illegal activities.
IV. Camera Trapping during Safaris: A Unique Experience
For tourists visiting Indian National Parks, camera trapping offers a unique and immersive experience. Many eco-tourism initiatives now incorporate camera trapping as part of safari activities, allowing visitors to actively participate in wildlife conservation efforts.
During the safari, participants have the opportunity to set up camera traps under the guidance of trained professionals. They learn about camera placement strategies, data collection, and how to identify various species based on their tracks and behaviors. This hands-on experience creates a profound connection with nature, instilling a sense of responsibility towards wildlife conservation.
Moreover, tourists get to witness the results of their efforts, as the images and videos from the camera traps are shared with them during the safari or afterward. This interaction with raw wildlife footage, including glimpses of elusive creatures, adds excitement and meaning to their safari experience.
V. Learning from Camera Trapping
Participating in camera trapping activities provides numerous learning opportunities for tourists and even local communities:
Understanding Wildlife Behavior: Through camera trapping, participants gain insights into the behavioral patterns and ecological roles of various animal species. Understanding the natural behaviors of wildlife is crucial for promoting empathy and informed decision-making regarding conservation.
Conservation Awareness: Engaging in camera trapping encourages tourists and locals to become active stakeholders in wildlife conservation. Witnessing the importance of protecting wildlife firsthand fosters a deeper appreciation for the interconnectedness of nature.
Citizen Science Contribution: Tourists and locals involved in camera trapping activities become citizen scientists, contributing valuable data to ongoing research and conservation projects. This collaboration strengthens conservation efforts and fosters a sense of collective responsibility towards preserving India's rich biodiversity.
Camera trapping has emerged as a game-changing tool for wildlife conservation in Indian forests. Its non-intrusive and technology-driven approach provides crucial data for the Forest Department to make informed decisions in protecting the country's precious fauna. Additionally, by involving tourists in camera trapping activities during safaris, a unique and educational experience is created, fostering a sense of stewardship towards wildlife and ecosystems. Embracing this innovative approach to wildlife monitoring and eco-tourism will undoubtedly play a vital role in preserving India's natural heritage for generations to come.