The Role of Forest Corridors in India: How They Impact Wildlife Safari in India
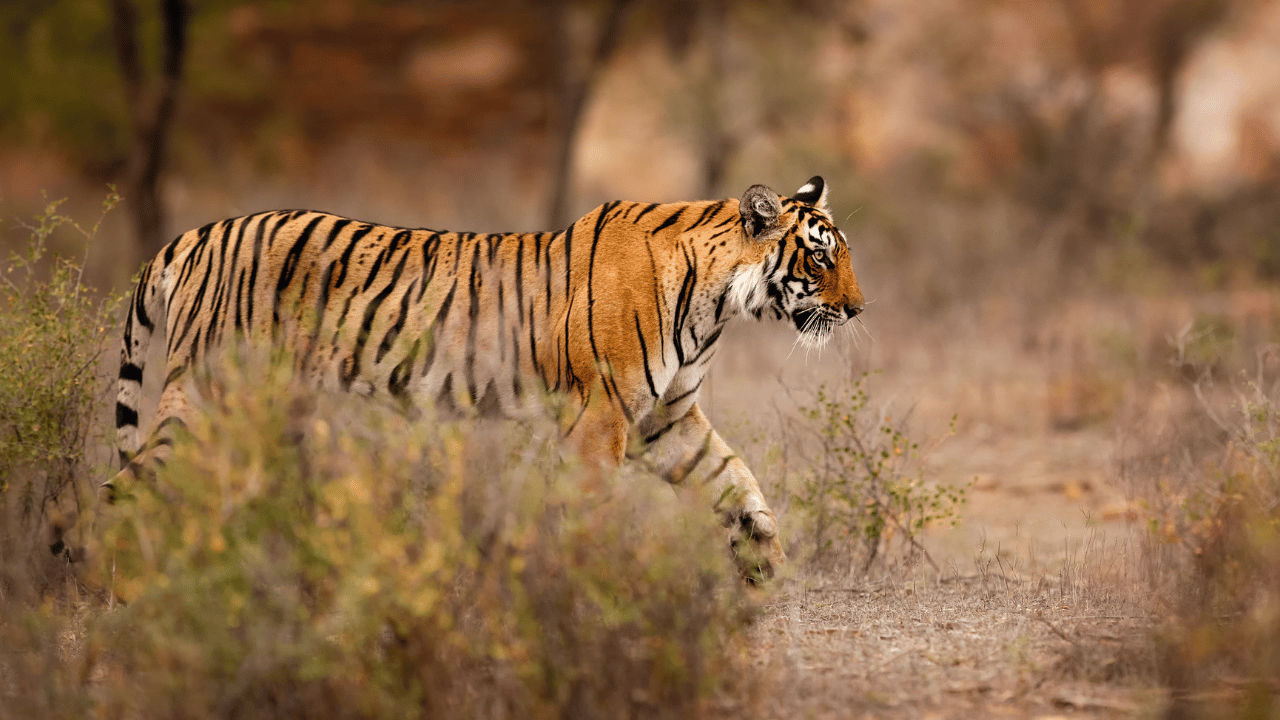
India is home to a vast and diverse ecosystem, supporting some of the most iconic wildlife species in the world. From the majestic Bengal tiger to the gentle Asian elephant, the country's forests provide a crucial habitat for countless species. However, habitat fragmentation due to human activities poses a serious threat to wildlife. This is where forest corridors come into play. These vital passageways help connect fragmented habitats, ensuring the free movement of wildlife and promoting biodiversity.
One of the major attractions for nature enthusiasts is the wildlife safari in India, which allows visitors to witness these magnificent creatures in their natural habitat. But without well-maintained forest corridors, the future of wildlife safaris and conservation efforts is at risk.
Understanding Forest Corridors
What are Forest Corridors?
Forest corridors are natural or man-made pathways that connect isolated forest patches, allowing animals to migrate safely between habitats. These corridors help maintain genetic diversity, reduce inbreeding, and prevent human-wildlife conflicts.
Why are Forest Corridors Important?
-
Preserve Genetic Diversity – Ensuring species survival by preventing inbreeding.
-
Facilitate Wildlife Movement – Allowing species to migrate in search of food, mates, and better habitats.
-
Reduce Human-Animal Conflict – Preventing animals from entering human settlements.
-
Enhance Biodiversity – Supporting a wide range of plant and animal species.
Types of Forest Corridors in India
India has several types of forest corridors, each serving a unique purpose:
-
Terrestrial Corridors – Pathways connecting two land-based forest patches.
-
Riverine Corridors – Forested areas along rivers that act as natural movement routes.
-
Riparian Corridors – Ecosystems along water bodies providing safe passage for wildlife.
Key Forest Corridors in India
Some of the most crucial forest corridors in India include:
-
Kanha-Pench Corridor (Madhya Pradesh-Maharashtra) – Used by tigers and leopards.
-
Kaziranga-Karbi Anglong Corridor (Assam) – Ensures elephant and rhino movement.
-
Sathyamangalam-Mudumalai Corridor (Tamil Nadu) – Supports elephant migration.
-
Nilgiri Biosphere Corridor (Tamil Nadu-Kerala-Karnataka) – Home to tigers, elephants, and other species.
These corridors play a significant role in sustaining a successful wildlife safari in India, offering a glimpse of animals in their natural environment.
Importance of Forest Corridors for Wildlife
1. Ensuring Genetic Diversity
Isolated animal populations suffer from inbreeding, leading to genetic defects. Corridors allow genetic exchange, ensuring healthier populations.
2. Reducing Human-Animal Conflict
Without safe passage, animals stray into villages, leading to conflicts. Corridors keep them within protected zones.
3. Supporting Seasonal Migrations
Many species, like elephants and tigers, require large territories. Corridors help them migrate safely without disturbances.
Wildlife Species Benefiting from Corridors
Some of the most well-known species benefiting from forest corridors include:
-
Bengal Tiger – Uses corridors for hunting and mating.
-
Asiatic Elephant – Migrates long distances through corridors.
-
Indian Leopard – Moves between fragmented habitats for survival.
-
Sloth Bear – Uses dense vegetation corridors for protection.
These species are a major attraction for wildlife safaris in India, making corridors essential for tourism as well.
Threats to Forest Corridors in India
Despite their importance, forest corridors face several threats:
-
Deforestation – Clearing forests for agriculture and settlements.
-
Urbanization – Expanding cities encroaching on natural habitats.
-
Infrastructure Development – Highways and railways disrupting animal movement.
-
Poaching and Illegal Activities – Endangering species dependent on corridors.
Conservation Efforts for Forest Corridors
Several organizations and government initiatives are working to protect these corridors:
-
Project Elephant – Ensuring safe migratory routes for elephants.
-
National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA) – Monitoring tiger movement through corridors.
-
NGO Initiatives – Wildlife Trust of India, WWF, and other groups working for corridor conservation.
The Future of Forest Corridors in India
With increasing awareness and conservation efforts, India is actively working on restoring and protecting forest corridors. Future projects include:
-
Creating More Protected Areas – Expanding wildlife reserves.
-
Implementing Green Bridges – Building eco-friendly overpasses for animals.
-
Strengthening Laws – Stricter regulations against deforestation and illegal encroachment.
FAQs on Forest Corridors and Wildlife Safari in India
? How do forest corridors affect wildlife safaris in India?
? They ensure a richer wildlife experience by allowing animals to roam freely.
? What is the biggest threat to forest corridors in India?
? Deforestation and urbanization are the major threats.
? Can tourists help in corridor conservation?
? Yes! Choosing eco-friendly safaris and supporting conservation programs can help.
? Which national parks in India benefit from forest corridors?
? Kaziranga, Jim Corbett, Bandipur, and Kanha are some examples.
? Are there government policies to protect forest corridors?
? Yes, initiatives like the Wildlife Protection Act and NTCA support corridor conservation.